Could we ever have a lot of chamomile plants in home? No, I really don’t think so!
Luckily, you do not need to spend a fortune to get as many lavenders as you desire, however you can propagate them. And guess what’s for free!
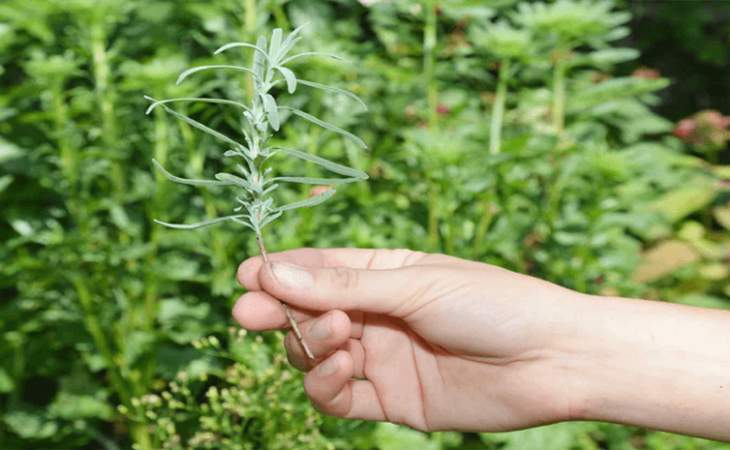
It’s possible to propagate lavenders really simple. You simply need a proven lavender plant along with some patience. Only 1 lavender plant may provide you heaps more at no cost. Plus it works for all sorts of lavenders.
Whether or not you wish to propagate from stem trimming or out of seeds, in this article you’ll be able to get the directions on how to perform it.
Propagation with Cuttings
It’s possible to propagate lavender out of hardwood or softwood cuttings.
The hardwood cutting is thick and does not bend. This may snap if you’re working to bend. Hardwood cuttings have a woody stem and all these will be the old regions of the lavender. These ought to be collected in fall or spring.
Softwood cuttings are out of the tender, bendy hints of this new expansion. You can have lots of softwood cuttings throughout the spring and you’ll be able to cut them without destroying or disturbing the plant.
The drawback of collecting softwood cuttings is these are less dependable as hardwood cuttings. But, softwood cuttings will trigger faster.
How to Take Cuttings?
When picking the stem for cuttingedge, make certain there’s not any blossom on it. You must always cut on a stem which has just left since the blossoms can choose the energy of this plant and it’s low likelihood it will develop roots. This stem will revolve around blooming, instead of developing roots.
You always need to select a healthful, right and vigorous stem which has good colour and no buds. With a sharp knife and choose the hardwood or softwood cuttingedge. These ought to be 3 to 4 inches.
Always use an extremely sharp knife, since the scissors along with a blunt knife will shut the stem from the location where you’re cutting it. This can make cleanup hard.
So, cut on the wood stem just below a leaf node. That’s the node in which the leaves grow from. Remove the leaves from the stem. You simply want the leaves towards the cover of the stem, because these can help the cleanup.
Then it is possible to adhere the lower end of the cutting into the prepared soil. Bear in mind, you have to set them in the dirt at precisely the exact same way the plant has been growing. Thus, keep an eye on which side is the base.
The dirt ought to be well-draining dirt and you’re able to use rooting hormone to boost the rooting process.
After planting the cuttings, place a plastic bag over the pot, which means that you may provide a greenhouse impact in their opinion.
How to Care for Lavender Cuttings?
As I mentioned previously, softwood cutting will probably trigger faster than hardwood cuttings. Softwood cuttings can develop roots in just two to three weeks.
If it comes to the hardwood cuttings, you need to check them frequently because these require somewhat longer. Every other day you’re able to pull mild the cuttings. If you feel resistance, it means that there are a few roots grown.
If the roots have been formed, remove the plastic bag.
Set the pot in a bright place and warm water it just when the upper inch (3 cm) of the ground is dry.
You could even fertilize it to assist the plant to develop new roots, but if you utilize commercial dirt, the containing nutrients must be sufficient for your new plants.
After the cuttings develop follicles, you are able to restate them into different and bigger pots.
Propagating lavender plants from cuttings is the simplest approach. Success is much more likely to occur than growing plants from seeds. However, to have cuttings, you need to get a plant.
If you do not wish to purchase one since you’ve seeds or you simply enjoy struggles, then this really is the way to propagate lavender plants .
Propagation from Seeds
The lavender seeds can be bought from stores, or gathered from plants.
If you would like to accumulate them, you ought to do it after flowering, once the flowers faded along with the seeds pods dried out entirely.
If you shake the plant, then the seeds will drop from the pods. That is when you need to collect them.
You ought to sow the seeds every time you prefer from February to July. Utilizing moist seed compost, place the seeds onto the surface and sprinkle them for covering a few vermiculite or finely sieved compost.
Set the pot in a sunny and warm place, or so the dirt won’t be too moist and the seeds will probably get sufficient warmth.
You have to provide the warmth of 65 to 70° F/ 18 to 21° C to guarantee germination. It may take you to three months for the seeds to germinate, so be patient.
But as soon as the lavender seeds have many leaves, then you can transplant them .
Air Layering Propagation
Spring is the ideal time to propagate with this technique since the lavender plant is in active development.
Air layering propagation is the ideal way to select if you would like to place the least effort in to propagation, but it may be carried out only on a healthier plant that is established.
Thus, select a low-growing stem in your own healthy plant and then bend the center of the stem to the floor. Remove the foliage out of the center part of the stem and create a shallow wound onto the lower side, that will touch the floor.
Then sprinkle the wound together with rooting hormone and then bury the injured portion of the stem to the floor (1-2 inches).
To keep it in place, place a rock on it “basic” it using a bit of stainless steel. These stalks should cause about fourteen days.
After rooting, you are able to cut off the stem and transplant it, wherever you want, in well-draining soil.
Wrap Up
Propagating lavender plants isn’t tough. This is sometimes carried out with cuttings, sowing seeds or atmosphere abounds.
Propagation from cuttings and air layering will provide faster results and the plant will probably be accurate to the original plants.
Growing lavender out of seeds can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. On the other hand, the plant could be different in the original plant.